Quotation
From Supply Chain Management Encyclopedia
Russian: Коммерческое предложение
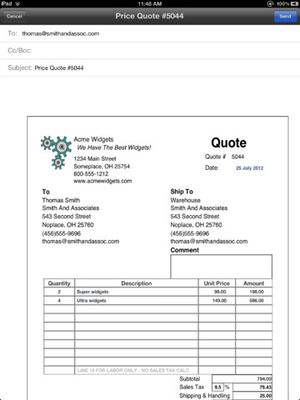
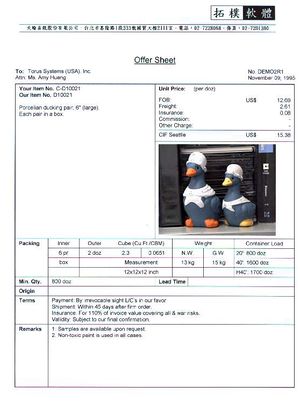
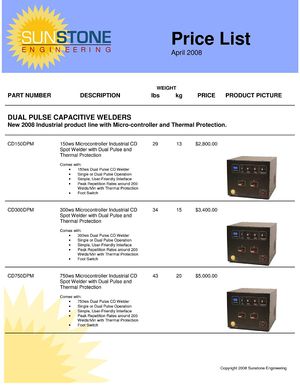
Quotation (offer) is a trade document which, with a view to concluding a contract, sets out the conditions under which the goods are offered. In exporting, the terms quote, offer sheet and price sheet/list may be used instead of quotation. [See samples below.] The basic information that an export quotation should have includes a description of goods, trade terms (e.g. FOB, CFR or CIF), unit price, packing (packaging), means of delivery (e.g. ocean or air), delivery time, and payment terms. No strict form is used in the quotation. Using the company letterhead for a general quotation is quite common.[1] In international trade practices, quotation (and its options - See above) and offer terms are often using interchangeably. However, in accordance with main official documents governing the process of offering [2][3]these terms are not synonyms for official documents. The main distinction of quotation versus an offer is that the first term is referenced rather as an analogue of a free rather than the firm offer.
Примеры коммерческих предложений
Instructions for Preparing the Export Quotation Worksheet[4]
The Export Quotation Worksheet serves to ensure that all items of cost in the fulfillment of the transaction are made known, as appropriate, included into the full quotation offered to the prospective buyer.
- Provide a brief but clear description of the product has to be a subject of the transaction expected.
- State the country of destination to which the seller has to consign the goods.
- Indicate the terms of payment for the goods taking into account any costs the seller might incur based on the payment term.
- Propose the rule of Incoterms (2010) – necessary to calculate delivery costs.
- State exactly the point of delivery (in accordance with the rule of Incoterms).
- Assign the unique reference (number/letter code) to this transaction and corresponding supporting documents.
- Determine approximate physical dimensions, gross weight an total cube – necessary to define transportation costs.
- Propose a mode of transportation for the main carriage or an intermodal one (in accordance with the rule of Incoterms).
- Total proposed selling price for the product itself.
- Cost of special export packing/crating (if any) requested by the byer or required for the movement of the goods.
- Costs of pre-carriage (in accordance with the rule of Incoterms) to get to the initial point of the main (international) carriage.
- Costs of the main carriage (all surcharges and other ancillary fees/charges has to be included).
- Costs of cargo insurance. In the case of CIP or CIF, this amount may be presented in the separate line. If the seller pays the cargo insurance, this amount may be included in the price of the goods.
- Determine and indicate any other fees and charges could be arisen in concluding the transaction.
- Total amount sought to be recovered from a prospective buyer for the present transaction.
See also: Commercial offer
References
- ↑ Export-Import Quotations | http://www.export911.com/e911/export/quote.htm
- ↑ United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods, Vienna, 11 April 1980, S.Treaty Document Number 98-9 (1984), http://www.uncitral.org/uncitral/en/uncitral_texts/sale_goods/1980CISG.html at 22 December 2007.
- ↑ UNIDROIT Principles of International Commercial Contracts 2010 - http://www.unidroit.org/english/principles/contracts/principles2010/integralversionprinciples2010-e.pdf
- ↑ Compiled on the basis of materials revealed at http://www.unzco.com/forms/instructions/EQWinstructions.pdf