Open Account
From Supply Chain Management Encyclopedia
(→Principal Flow Chart of Open Account Payment with Components of Export Credit Risk Management) |
(→Principal Flow Chart of Open Account Payment with Components of Export Credit Risk Management) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
* 2) In parallel with delivering goods under the said sale contract, the exporter (A) issues the appropriate invoice. | * 2) In parallel with delivering goods under the said sale contract, the exporter (A) issues the appropriate invoice. | ||
* 3) Having received the said goods, the importer (B) has a right to defer a payment for a stipulated period (usually, from 30 to 90 days) and then transfers the payment under the said sale contract to the exporter (A). (The case of non-acceptancy under non-conforming to quantity/quality terms is excluded from consideration herein.) | * 3) Having received the said goods, the importer (B) has a right to defer a payment for a stipulated period (usually, from 30 to 90 days) and then transfers the payment under the said sale contract to the exporter (A). (The case of non-acceptancy under non-conforming to quantity/quality terms is excluded from consideration herein.) | ||
| + | |||
| + | On the one hand, the open account terms are highly risky for exporters and, on the other hand, in order to compete in competitive markets exporters have to offer these open account terms to attract importers. Therefore, to resolve this contradiction, exporters are searching for export credit protection means. A pair of such means is presented below<ref> Trade Finance Guide: A Quick Reference for U.S. Exporters – International Trade Administration, U.S. Department of Commerce, Washington, April, 2008 - p.12. - http://trade.gov/publications/pdfs/tfg2008.pdf </ref>: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Export credit insurance – this techniques provides protection against commercial risks <ref> Commercial risks include bankruptcy, receivership, and other kinds of insolvencies, as well as protracted defaults caused by cash flow problems, balance sheet issues, bad faith, market demand, currency fluctuations, natural disasters, or general economic conditions in your customer's country or abroad. - Export credit insurance - http://www.meridianfinance.com/export_credit.html </ref> and political risks <ref> Political risks include currency inconvertibility, foreign exchange controls, transfer risks, war, strikes, riots, revolution, confiscation, expropriation, nationalization, embargoes, trade sanctions, and changes in import or export regulations. – ibid.</ref> (such as war, nationalization, and currency inconvertibility). It allows exporters to increase sales by offering liberal open account terms to new and existing customers. Insurance also provides security for banks that are providing working capital and are financing exports. | ||
=='''References'''== | =='''References'''== | ||
Revision as of 09:43, 31 July 2014
Russian: Открытый счет
General Provisions
In an Open Account transaction, the exporter conducts international business in a manner similar to the way it conducts business domestically[1]. The exporter just sends an invoice to the importer along with the shipment and trusts the customer to pay within a reasonable amount of time, commensurate with the credit usually granted in the country in which the importer operates, usually thirty to ninety days. It is essentially the conceptual opposite of Cash in Advance, as the exporter shows complete trust in the importer and ships the merchandise without any guarantee that it will be paid. The only recourse in case of non-payment is legal action in the importing country, a time-consuming and expensive process that exporters rarely undertake. This open account method should be reserved to established customers, or customers with whom the exporter expects to have an ongoing relationship. It could possibly be extended to new orders from large companies and/or companies for which commercial credit data is available, and whose credit rating is excellent. This open account method should be reserved to established customers, or customers with whom the exporter expects to have an ongoing relationship. It could possibly be extended to new orders from large companies and/or companies for which commercial credit data is available, and whose credit rating is excellent[2].
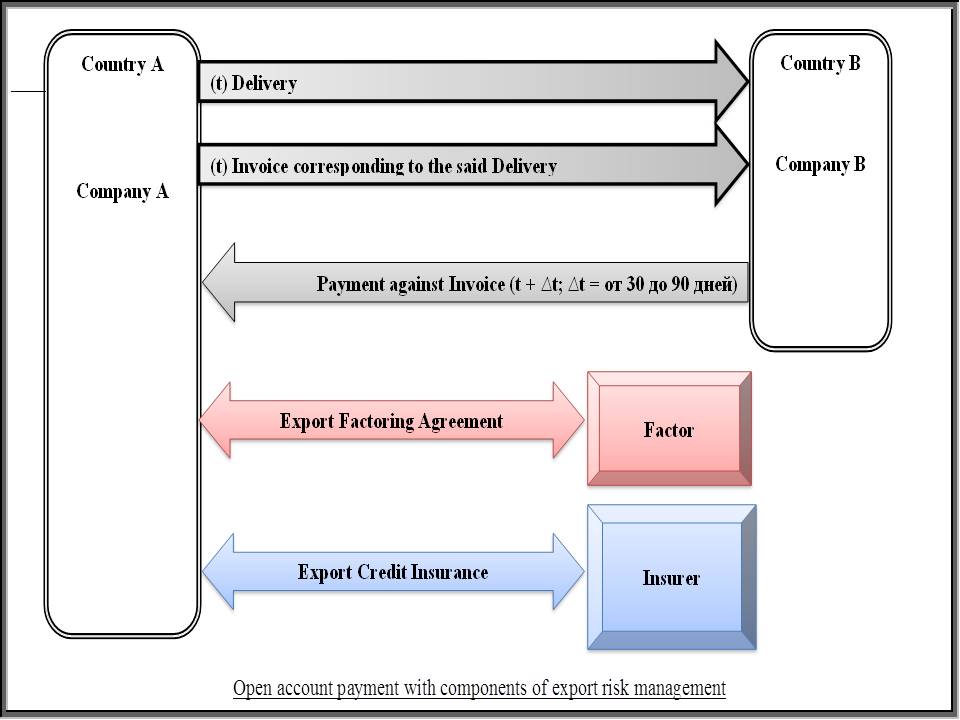
Principal Flow Chart of Open Account Payment with Components of Export Credit Risk Management
LEGEND:
- 1) After having the sale contract concluded, the exporter (A) ships goods to the importer(B).
- 2) In parallel with delivering goods under the said sale contract, the exporter (A) issues the appropriate invoice.
- 3) Having received the said goods, the importer (B) has a right to defer a payment for a stipulated period (usually, from 30 to 90 days) and then transfers the payment under the said sale contract to the exporter (A). (The case of non-acceptancy under non-conforming to quantity/quality terms is excluded from consideration herein.)
On the one hand, the open account terms are highly risky for exporters and, on the other hand, in order to compete in competitive markets exporters have to offer these open account terms to attract importers. Therefore, to resolve this contradiction, exporters are searching for export credit protection means. A pair of such means is presented below[3]:
- Export credit insurance – this techniques provides protection against commercial risks [4] and political risks [5] (such as war, nationalization, and currency inconvertibility). It allows exporters to increase sales by offering liberal open account terms to new and existing customers. Insurance also provides security for banks that are providing working capital and are financing exports.
References
- ↑ David, P.A., Stewart, R.D. International Logistics: The Management of International Trade Operations – Cengage Learning, 2010 – p.142.
- ↑ ibid.
- ↑ Trade Finance Guide: A Quick Reference for U.S. Exporters – International Trade Administration, U.S. Department of Commerce, Washington, April, 2008 - p.12. - http://trade.gov/publications/pdfs/tfg2008.pdf
- ↑ Commercial risks include bankruptcy, receivership, and other kinds of insolvencies, as well as protracted defaults caused by cash flow problems, balance sheet issues, bad faith, market demand, currency fluctuations, natural disasters, or general economic conditions in your customer's country or abroad. - Export credit insurance - http://www.meridianfinance.com/export_credit.html
- ↑ Political risks include currency inconvertibility, foreign exchange controls, transfer risks, war, strikes, riots, revolution, confiscation, expropriation, nationalization, embargoes, trade sanctions, and changes in import or export regulations. – ibid.